
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Enterprise Resource Planning
- ERP Blogs by Members
- INTRASTAT reporting in S/4 HANA
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
About Intrastat Reporting
In January of 1993, European Union established a system to collect information on the intra-community trade of goods. This replaced the custom declaration requirement for the trade between member states. The idea was to enable ease of doing business within the EU as a single market. Subsequent regulation was passed in the January of 2005 with an aim to simplify the process of collecting reliable trade data from EU member countries and send the information to EU’s statistics office (Eurostat). This statistical report is used for example for determining the balance of payment and total figures of cross-border trade between different EU member countries.
The information from the business involved in intra EU trade is collected on a monthly basis by the authorities of respective EU member countries and then it is transmitted to Eurostat. Usually, each member country decides on an annual basis, a threshold value beyond which a business needs to submit this statistical report.
The content of the report (data elements) are very similar with some country specific requirements. The common data elements for arrivals and dispatches are as listed below:
- Business transaction type - This defines the type of cross border transaction. These are defined based on a two-digit numeric code. For example in Germany business transaction type ‘11’ represents a final purchase or sale transaction.
- Procedure - The procedure classifies the different arrivals and dispatches for statistical purposes. Example to differentiate import of goods for free circulation v/s temporary import of goods for further processing under contract.
- Consignment country - The EU member country from where the goods are shipped
- Country of destination - The EU member country where the goods will be consumed
- Destination region - The EU member country region where the goods will be consumed
- Country of origin - The simple definition of country of origin means the EU member country where the good is produced. Country of origin could be outside EU as well.
- Region of origin - The EU member country region where the good is produced
- Tare mass - Tare mass of the good (product)
- Description of goods - A brief description of the good (product)
- Customer/Supplier VAT registration number - VAT registration number of the customer in case of dispatch and VAT registration number of supplier in case of arrivals
- Incoterms - International commercial terms for delivery terms agreed between the consignor and consignee for the transaction. These terms are three character alpha codes as published by International Chamber of Commerce example FCA (Free Carrier).
- Currency of vendor - In case of arrivals the currency used by the supplier of the goods
- Invoice value - The total taxable value of the goods.
- Statistical value - The total value of the good (product) including freight, insurance costs.
- Commodity code - It is numeric code also known as Customs Tariff Code or CN8 which stands for Combined Nomenclature (at 8 digit level) used to classify goods (products).
- Supplementary unit - Depending on custom tariff code a supplementary unit of measure might be used, for example: pairs, dozens etc. to define the quantity or volume of the product.
- Mode of Transport - This is usually a single digit code representing the means of transport e.g. ‘2’ for rail, ‘3’ for road etc.
- Port/airport - These are country specific codes representing port and airports. For example the port Alicante Maritima situated in Spain has code “0311”.
Intrastat reporting in S/4 HANA
SAP Global Trade Services (GTS) is the go-to application for any foreign trade related services. However, there are customers who are using SAP ECC’s Foreign Trade/Customs Periodic Declarations components viz. SD-FT-GOV for dispatches and MM-FT-GOV for arrivals for Intrastat Reporting. For such customers moving to S/4 HANA, the option will be to use the Intrastat Reporting functionality provided under International Trade.
The S/4 HANA application is rebuilt by SAP with simplified data model. This has led to removal of functionalities under the foreign trade components SD-FT/MM-FT. In S/4 HANA some of the functionalities like product classification, legal control for export, embargo checks and Intrastat Reporting has been provided under International Trade which is part of Governance, Risk and Control (GRC) module in S/4 HANA.
S/4 HANA System Configuration for Intrastat Reporting
The required system configuration for Intrastat Reporting is mentioned below.
- Partner Country – The configuration related to partner country set-up is not available in SAP ECC system and it is new in S/4 HANA. These are brought over from SAP GTS to S/4 HANA. It provides mapping of the country of declaration with partner country with which trade is carried out. Also, provides the option of mapping exceptions related to partner countries depending on the country of declaration.
- Define Partner Country – Set up country codes for all relevant EU member countries for which Intrastat Reporting (arrivals/dispatch) needs to be carried out.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Partner Country > Define Partner Country (Object: /ECRS/V_TPCI; Tcode: SM30) 
- Assign Partner Country to Country of Declaration – In this step, assign the Country of Declaration (the EU member country where the business needs to declare Intrastat) to the partner country from where the goods are procured or sold.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Partner Country > Assign Partner Country to Country of Declaration (Object: /ECRS/V_TRAP; Tcode: SM30) 
- Define Exceptions for Mapping of Partner Country – Assigning partner country code based on the country of declaration. For example: If the declaration country is Ireland (IE) and the partner is from Antrim (AT) region, then Ireland does not recognise it as part of Great Britain (GB) instead it is considered as part of a separate country Northern Ireland (IX).
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Partner Country > Define Exceptions for Mapping of Partner Country (Object: /ECRS/V_TMPC; Tcode: SM30) 
- Country of Origin – The configuration related to country of origin set-up is not available in SAP ECC system and it is new in S/4 HANA. Similar to partner country set-up, this is brought over from SAP GTS to S/4 HANA. It provides mapping of the country of origin information based on the country of declaration.
- Define Country of Origin – Set up country codes for all countries including Non-EU countries.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Country of Origin > Define Country of Origin (Object: /ECRS/V_TCOO; Tcode: SM30)
- Assign Country of Origin to Country of Declaration – In this step, assign all country of origin to the relevant country of declaration where business needs to carry out Intrastat declaration.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Country of Origin > Assign Country of Origin to Country of Declaration (Object: /ECRS/V_TRCO; Tcode: SM30) 
- Define Exceptions for Mapping of Country of Origin – Assigning country of origin code based on the country of declaration. For example the country Monaco (MC) is not recognised as an independent sovereign country, but considered as part of France. Hence, in the report if the country of origin of the goods is Monaco (MC) it is substituted with country code France (FR).
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Country of Origin > Define Exceptions for Mapping of Country of Origin (Object: /ECRS/V_TMCO; Tcode: SM30)
- Region – The regions (codes) per country are defined. Information related to region is required in case of Belgium, Czech Republic, France, Germany, Italy, Portugal, Solvakia and Spain. Similar to partner country set-up, this is brought over from SAP GTS to S/4 HANA.
- Define Region – Set up all regions per country. The column “Relevance” is where the combination of country + region can be flagged if it is relevant only for “1 - Receipt” or “2 – Dispatch” or “blank – for both receipt & dispatch”.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Region > Define Region (Object: /ECRS/V_TRGI; Tcode: SM30)
- Define Mapping of Region – Mapping of regions is carried out under this configuration. The numerical code representing region is usually published by respective government authorities. For example Brandenburg region “BB” official intrastat code is “12
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Region > Define Mapping of Region (Object: /ECRS/V_TMRE; Tcode: SM30)
- Business Transaction Type – The codes representing the nature or type of business transaction is defined. This is a numerical code defined per country.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Define Business Transaction Type (Object: /ECRS/V_T605; Tcode: SM30) 
- Define Procedure – This is numerical code defined by relevant authorities per country
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Define Procedure (Object: /ECRS/V_T616; Tcode: SM30)
- Define Movement Code – These are special movement code as required for Czech Republic. This is new configuration table brought over from SAP GTS to S/4 HANA
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Define Movement Code (Object: /ECRS/V_TSMC; Tcode: SM30)
- Define Mode of Transport at the Border – These are single digit numerical code representing the mode of transportation. These codes are country specific.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Define Mode of Transport at the Border (Object: /ECRS/V_T618; Tcode: SM30)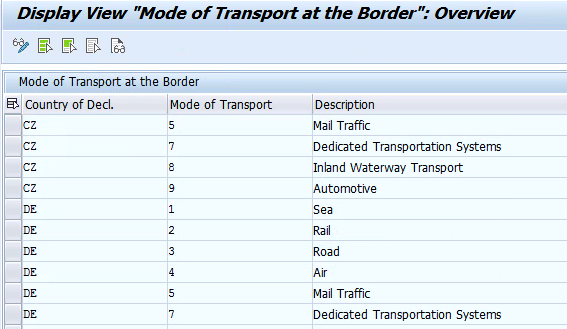
- Define Port and Airport – These are country specific codes representing a seaport or an airport. This configuration in S/4 HANA is brought over from SAP GTS. In SAP ECC system it is not available. YThe option in SAP ECC could be to set-up the seaports and airports under the configuration “Define Customs Office” (Object: V_T615), and further under the configuration “Define Valid Combinations: Mode of Transport - Customs Office” (Object: V_T618K) the combination of country + mode of transport and seaport/airport code used to be set-up.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Define Port and Airport (Object: /ECRS/V_TPRT; Tcode: SM30)
- Define Incoterms – INCO terms in this configuration is carried out based on country of INTRASTAT declaration with relevant description.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Define Incoterms (Object: /ECRS/V_TINC; Tcode: SM30)
- Define Collection Center – It is a code defined per country of declaration which represents the official centers in which Intrastat declarations from a region are collected. This configuration is not available in SAP ECC and it is brought over from SAP GTS to S/4 HANA.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Basic Data > Define Collection Center (Object: /ECRS/V_TCCE; Tcode: SM30)
- Default Values – Under these set of system configuration certain default data (values) are defined. The data can be defaulted in sales, purchasing related transactions as well as certain data value based on transportation data relevant for a transaction.
- Define Default Values for Sales – System can be configured to set default values in sales transaction for business transaction type, procedure and special movement code based on the combination of country of declaration, item category and the material group for intrastat reporting. The material group is defined and maintained in the material master.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Default Values > Sales > Define Default Values for Sales (Object: /ECRS/V_TDVS; Tcode: SM30)
*Proc. Dsp. or Cust. Ret. = Statistical procedure for Dispatches or Customer Returns
*Proc. Rcp. or Ret. Suppl. = Statistical procedure for Receipts or Returns to Supplier
- Define Material Group for Intrastat – Define the material group, which will be assigned to materials having similar Intrastat requirements.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Default Values > Sales > Define Material Group for Intrastat (Object: /ECRS/V_TVFM; Tcode: SM30)

- Define Default Values for Purchasing – System can be configured to set default values in purchasing transactions for business transaction type, procedure and special movement code based on the combination of country of declaration, purchasing document category, purchasing document type and item category for intrastat reporting. The material group is defined and maintained in the material master.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Default Values > Purchasing > Define Default Values for Purchasing (Object: /ECRS/V_T161B; Tcode: SM30)
- Define Business Transaction Type for Returns to Supplier – In this configuration object define the default business transaction type representing return of goods to supplier based on the combination of country of declaration and the business transaction type representing the receipt. For example in Austria (AT) the business transaction type code 1 represents “Final Purchase/Sale” based on the settings shown in below screenshot system will default business transaction type code 2 “Return of Goods” in case of return of goods to supplier.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Default Values > Purchasing > Define Business Transaction Type for Returns to Supplier (Object: /ECRS/V_TBTR; Tcode: SM30)
- Define Procedure for Returns to Supplier – In this configuration object define the default statistical procedure representing return of goods to supplier based on the combination of country of declaration and statistical procedure for receipts. For example in Austria (AT) the statistical procedure code 40000 represents “Final Receipt” based on the settings shown in below screenshot system will default statistical procedure 10000 “Final Dispatch” in case of return of goods to supplier.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Default Values > Purchasing > Define Procedure for Returns to Supplier (Object: /ECRS/V_TPRR; Tcode: SM30)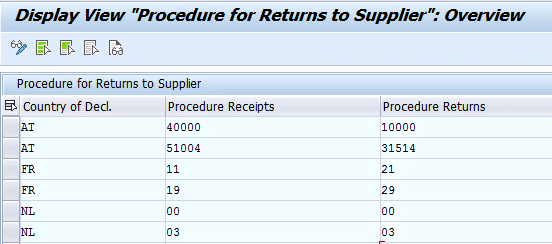
- Define Default Values for Transportation Data for Dispatches – This configuration is related to default values for mode of transport, seaport/airport code and country of the means of transport. The information regarding the country of the means of transport is required if the country of declaration is Bulgaria.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Default Values > Transportation Data > Define Default Values for Transportation Data for Dispatches (Object: /ECRS/V_T617_2; Tcode: SM30)
- Define Default Values for Transportation Data for Receipts – This configuration is related to default values for mode of transport, seaport/airport code and country of the means of transport for arrivals (receipts) transactions. The information regarding the country of the means of transport is required if the country of declaration is Bulgaria.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Default Values > Transportation Data > Define Default Values for Transportation Data for Receipts (Object: /ECRS/V_T617_1; Tcode: SM30)
- Define Default Values for Place of Delivery – This is a special configuration mainly required for Croatia and Slovenia. This set-up is not available in SAP ECC. In this configuration the name of the place of delivery can be defaulted based on the direction of the goods flow (1 – Receipt or 2 – Dispatch) and the specific INCO term.
The options for place of deliveries are:
- 1 Country of Declaration
- 2 Other Member State of EU
- 3 Outside EU
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Default Values > Define Default Values for Place of Delivery (Object: /CCEE/SIFIINCP3; Tcode: SM30)

- Data Selection Control – Under these set of system configuration country specific system logic can be set-up to select relevant transaction data for intrastat reporting. Besides additional configuration related to inclusion and exclusion of transactions from the report is also defined.
- Define Data Selection Control for Sales – This is country specific setting to select relevant sales transaction data based on the billing date or the goods issue date.
- “ ” Billing date
- “A”Goods Issue date
- Define Data Selection Control for Sales – This is country specific setting to select relevant sales transaction data based on the billing date or the goods issue date.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Data Selection Control > Define Data Selection Control for Sales (/ECRS/V_T609IS_2; Tcode: SM30)
- Define Data Selection Control for Purchasing – This is country specific setting to select relevant purchase transaction data based on the following options. This part of the configuration is similar to what is available in SAP ECC system under “Data Selection Control” (Object: V_T609IS)
- “ ” Report Goods Receipt; wait for Invoice Receipt - In this case the purchasing transaction is selected based on goods receipt, but if no invoice receipt exists then the transaction is flagged for reporting in next month.
- “A” Report Goods Receipt; wait for Invoice Receipt; Read Inbound Deliveries - The logic in this case to select the purchasing transaction is same as above for “ ” but additionally system checks inbound deliveries in order to fetch relevant declaration data.
- “B” Report Invoice Receipt - In this case the purchasing transaction is selected for reporting only if there has been an invoice receipt
- “C” Report Goods Receipt - In this case the purchasing transaction will be selected for reporting based on goods receipt, even though the invoice receipt might be pending.
Besides the above there are additional check boxes which further adds to the selection logic for reporting. These additional checks mentioned below are not available in SAP ECC instead enhancement FTGOVSEL is available for any additional logic to be implemented for data selection.
- Selection by Document Date - If selected then the system logic will be to select purchasing transactions based on the document date and the goods receipt or invoice receipt posting dates are not relevant.
- Exchange Rate Date w/o Invoice - If selected then the system logic influences the date based on which the currency conversion rate is to be selected. This affects transactions, which is to be reported based on goods receipt and invoice receipt. So, if the invoice receipt is not carried out in the same period (as that of goods receipt) and the transaction is flagged to be reported in the following month then the currency conversion rate will be determined based on the 15th day of the following month (reporting month). For example
Goods receipt on: 20.02.2019
Invoice receipt on: 10.03.2019
Date for currency conversion rate will be 15.03.2019
- Exchange Rate Date Inv. In Prev. Month - If selected then the system logic influences the date based on which the currency conversion rate is to be selected. This affects transactions, which is to be reported based on goods receipt and invoice receipt. So, if the invoice receipt is carried out in a period before the goods receipt then the currency conversion rate will be determined based on the goods receipt date. For example
Goods receipt on: 10.03.2019
Invoice receipt on: 27.02.2019
Date for currency conversion rate will be 10.03.2019
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Data Selection Control > Define Data Selection Control for Purchasing (Object: /ECRS/V_T609IS_1; Tcode: SM30)
- Define Exceptions for Inclusion and Exclusion of Country and Region – Based on the country of declaration certain partner countries and/or regions can be flagged either as included or excluded from intrastat reporting. Similar setting related to inclusion/exclusion can be carried out in SAP ECC system under “Special Rule Country / Region” (Object: V_T609II). For example Monaco is not a member state of the European Union. However, dispatches to and receipts from Monaco as a partner country for Germany needs to be included in the intrastat report. Whereas the Spanish province of Santa Cruz de Tenerife to be excluded in the Germany intrastat report.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Data Selection Control > Define Exceptions for Inclusion and Exclusion of Country and Region (Object: /ECRS/V_T609II; Tcode: SM30)
- Define Exclusion of Sales Document Item Category – Under this configuration certain item categories from sales related transactions can be excluded from the intrastat reporting. Example a text item to be excluded in that case the corresponding item category can be maintained in this configuration table. Similar configuration is available in SAP ECC under “Assign to Item Categories for SD Sales Orders” (Object: V_TVAP_MAB) and “Assign to Item Categories for SD Deliveries” (Object: V_TVLP_MAB).
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Data Selection Control > Define Exclusion of Sales Document Item Category (Object: /ECRS/V_TICX; Tcode: SM30)
- Define Sales Document Item Category for Services – Except Italy, for all other EU member countries the sales of service related transactions are excluded from the intrastat report. Under this configuration all service relevant item categories are maintained in the table which are then excluded from intrastat reporting.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Data Selection Control > Define Sales Document Item Category for Services (Object: /ECRS/V_TICS; Tcode: SM30)
- Define Residence Time for Intrastat Declarations – The released intrastat declaration are moved to cold area after certain number of days as defined in this table. The number of days are defined based country of declaration and calculated from the first day of the month following the declaration month. This setting is not available in SAP ECC.
IMG path: Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Data Aging > Define Residence Time for Intrastat Declarations (Object: /ECRS/V_TRPA; Tcode: SM30)
- Business Add-Ins for Intrastat – There are three business add-ins (BAdIs) are provided for additional custom logic as might be required for intrastat reporting. The BAdIs are:
- Additional Item Checks in Intrastat Declaration (/ECRS/RP_CHECK_ITEM) - This can be used to incorporate custom logic for additional checks for the items in Intrastat declaration report
- Use the Intrastat Declaration File in Automatic Dispatch (/ECRS/RP_FILE_TRANSFER) - This can be used to load the file with the Intrastat declaration from the local data store into the system and send it as an e-mail attachment. This can also be used for adding the intrastat declaration file as an attachment.
- Intrastat Data Selection (BADI_INTRASTAT_SELECTION) - This can be used to add additional custom logic for selection of data related to intrastat reporting.
Now, moving from the system configuration steps to generating an intrastat report. The steps provided below are on high level. The data and set-up discussed in this blog are dummy and do not necessary represents the official set-up.
The Provider of info (masterdata) in S/4 HANA represents the company and the relevant plants for which the intrastat report is to be generated.
- Define Provider of Information - This represents the organization responsible for declaring intrastat report to the relevant authorities. This is one time activity (master data)
SAP Menu: Logistics > Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Manage Providers of Information (Tcode: /ECRS/POI_EDIT)
The detail view is shown in the below screenshot. Some of the important settings are as mentioned below:
- Exchange rate type: The exchange rate type to be used for reporting is specified here.
- Declaration File Format: There are two possibilities either an XML file or an ASCII file format. Based on the file format specified here the intrastat report will be generated accordingly.

Alternatively, one can use the Fiori App called “Manage Provider of Information”. In order to use this app the business role “SAP_BR_INTRASTAT_SPECIALIST” needs to be assigned to the user.


- Select Dispatches and Customer Returns - This is the same transaction as available in SAP ECC, but the selection option in S/4 HANA is very limited. The report selection screen is completely changed.
SAP Menu: Logistics > Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Select Dispatches and Customer Returns (Tcode: VE01).
Based on the “Provider of Info”, which has the assignment of relevant company codes and plants system will fetch all relevant dispatch and customer returns transaction based on the specified period. For the example I have taken a period in past (year 2018; month 12) for which report is not released as of now.
Click EXECUTE (F8)

The pop-up box shows how many dispatch transactions are selected for reporting. In the example 8 transactions were selected.

Alternatively, you can use the Fiori App called “Select Dispatches and Customer Returns”. In order to use this app the business role “SAP_BR_INTRASTAT_SPECIALIST” needs to be assigned to the user.
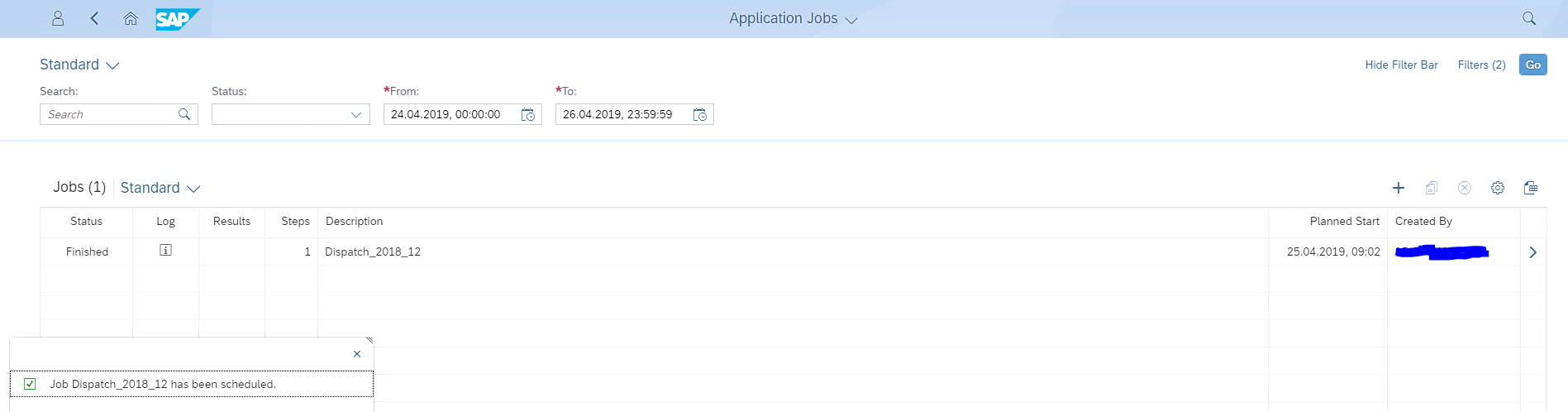
The app enables triggering of a background job for data selection for arrivals/dispatch based on the Provider of Information selected.

Once the job is executed the status and the log appears on the screen as shown below
- Select Receipts and Returns to Supplier - This is the same transaction as available in SAP ECC, but the selection option in S/4 HANA is very limited. The report selection screen is completely changed.
SAP Menu: Logistics > Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Select Receipts and Returns to Supplier (Tcode: MEIS)
Based on the “Provider of Info”, which has the assignment of relevant company codes and plants system will fetch all relevant arrival and return to supplier transaction based on the specified period. For the example I have taken a period in past (year 2018; month 12) for which report is not released as of now.
Click EXECUTE (F8)

The pop-up box shows how many arrivals transactions are selected for reporting. In the example 11 transactions were selected.

Similar to Fiori app “Select Dispatches and Customer Returns” there is an app called “Select Receipts and Returns to Supplier” as an alternative to SAP GUI transaction MEIS mentioned above.
- Manage Intrastat declaration - This is the only transaction in S/4 HANA which gives an overview of all intrastat report in process or released for submission. There are different functionalities available within this report viz reviewing the transactions for reporting, completeness check for the required data, releasing the report and generating required file for submission.
SAP Menu: Logistics > Governance, Risk and Compliance > International Trade > Intrastat > Manage Intrastat Declarations (Tcode: /ECRS/RP_EDIT)
- Provider of info. Represents the company (organization) responsible for reporting intrastat. For example “GERMANY” is defined as the provider of the information.
- Select all declaration flag if selected then system will fetch intrastat report both from cold as well as hot area. Remember based on intrastat residence time (in days) the released intrastat reports are moved to cold area.
Press ENTER.

Based on “Provider of Info” system has selected transactions relevant for country of declaration Germany.

Now let’s select the report from year 2018 period 12. The report status is “In process” as of now. In order to see the details, one of the option is to double click the row and the system opens up the detail view.
Under the “Selection Criteria”, there are various filter options. The “Incorrect” and “Correct” check box means system will select list of transaction items, which are incomplete (missing data) and complete data respectively. In the below screenshot note that none of the items are complete (column “Correct” not flagged).

To verify missing data at item level double click one of the items. In the below example the commodity code (Tariff code or CN8) is missing for the material (product).

Once the commodity code (tariff code) is specified you can re-check the correctness by clicking on the “Check item” icon or press Shift+F8 keys. The item gets updated and the check box “Correct” is now flagged. SAVE and click on green back arrow button or press F3 key to go back to the Change Intrastat Declaration: Item overview screen.

The Change Intrastat Declaration: Item overview screen shows the item with commodity code and also that the data is complete (refer the checkbox under column “Correct”).

Once all the data is corrected, you can go back to the overview screen and release the intrastat report and also generate the required file for reporting. In case of Germany as country of declaration the “.ASC” file is generated as per the settings mentioned in the data provider “GERMANY” masterdata.

As an alternative to above SAP GUI transaction there is a Fiori app called “Manage Intrastat Declaration” which can be used as well. It has same functionality as in case of GUI transaction. In order to use this app the business role “SAP_BR_INTRASTAT_SPECIALIST” needs to be assigned to the user.



The example and screenshots in this blog are based on S/4 HANA 1809 release. I hope the blog gives a good overview about Intrastat reporting using S/4 HANA International Trade module.
* This article is based on my personal opinion and does not necessarily represent the views of companies I am affiliate with.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP S/4HANA
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
"mm02"
1 -
A_PurchaseOrderItem additional fields
1 -
ABAP
3 -
abap cds
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
2 -
ABAP CDS Views - BW Extraction
1 -
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
1 -
ABAP Development
1 -
ABAP Extensibility
1 -
ABAP Programming
1 -
abapGit
1 -
ACCOSTRATE
1 -
ACDOCP
1 -
Adding your country in SPRO - Project Administration
1 -
Advance Return Management
1 -
AI and RPA in SAP Upgrades
1 -
API and Integration
1 -
Approval Workflows
1 -
Ariba
1 -
ARM
1 -
ASN
1 -
Asset Management
1 -
Associations in CDS Views
1 -
auditlog
1 -
Authorization
1 -
Auto PO from GR
1 -
Availability date
1 -
Azure Center for SAP Solutions
1 -
AzureSentinel
2 -
Bank
1 -
BAPI_SALESORDER_CREATEFROMDAT2
1 -
Billing
1 -
BRF+
1 -
BRFPLUS
1 -
Bundled Cloud Services
1 -
business participation
1 -
Business Processes
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Carbon
1 -
CDS Annotations
1 -
Cental Finance
1 -
CFIN
1 -
CFIN Document Splitting
1 -
Cloud ALM
1 -
Cloud Integration
1 -
COGS SPLIT
1 -
condition contract management
1 -
Connection - The default connection string cannot be used.
1 -
Consignment Process using MRP Area
1 -
Custom Table Creation
1 -
Customer Screen in Production Order
1 -
Customizing
1 -
Data Quality Management
1 -
Date required
1 -
Decisions
1 -
desafios4hana
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
3 -
Direct Outbound Delivery
1 -
DMEEX
1 -
DMOVE2S4
1 -
DTW
1 -
EAM
1 -
EDI
3 -
EDI 850
1 -
EDI 856
1 -
edocument
1 -
EHS Product Structure
1 -
Emergency Access Management
1 -
Employee Central Integration (Inc. EC APIs)
1 -
Energy
1 -
EPC
1 -
FINANCE
1 -
Financial Operations
1 -
Find
1 -
FINSSKF
1 -
Fiori
1 -
FIORI MY-INBOX
1 -
Flexible Workflow
1 -
Gas
1 -
Gen AI enabled SAP Upgrades
1 -
General
1 -
generate_xlsx_file
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
HomogeneousDMO
1 -
How to add new Fields in the Selection Screen Parameter in FBL1H Tcode
1 -
IDOC
2 -
integration
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
Ledger Combinations in SAP
1 -
LogicApps
2 -
low touchproject
1 -
Maintenance
1 -
Management
1 -
Material creation
1 -
Material Management
1 -
MD04
1 -
MD61
1 -
methodology
1 -
Microsoft
2 -
MicrosoftSentinel
2 -
Migration
1 -
Migration Cockpit
1 -
mm purchasing
1 -
MRP
1 -
MS Teams
3 -
MT940
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
Notifications
1 -
Oil
1 -
open connectors
1 -
Order Change Log
1 -
ORDERS
2 -
OSS Note 390635
1 -
outbound delivery
1 -
outsourcing
1 -
Payment medium
1 -
PCE
1 -
Permit to Work
1 -
PIR Consumption Mode
1 -
PIR's
1 -
PIRs
1 -
PIRs Consumption
1 -
PIRs Reduction
1 -
Plan Independent Requirement
1 -
POSTMAN
1 -
poultry in s4hana
1 -
Premium Plus
1 -
pricing
1 -
Primavera P6
1 -
Process Excellence
1 -
Process Management
1 -
Process Order Change Log
1 -
Process purchase requisitions
1 -
Product Information
1 -
Production Order Change Log
1 -
Purchase Blanket Agreement
1 -
purchase order
1 -
Purchase requisition
1 -
Purchasing Lead Time
1 -
QUERY SQL
1 -
Query View
1 -
Redwood for SAP Job execution Setup
1 -
RISE with SAP
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
Rizing
1 -
S4 Cost Center Planning
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
s4 hana public cloud
1 -
S4Hana
3 -
S4HANA Private Cloud
1 -
S4HANACloud audit
1 -
Sales and Distribution
1 -
Sales Commission
1 -
sales order
1 -
SAP
2 -
SAP Basis
1 -
SAP Best Practices
1 -
SAP Build
1 -
SAP Build Apps
1 -
SAP Business One
2 -
SAP Business One Service Layer
1 -
SAP CI
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration
1 -
SAP CPI
1 -
SAP CPI (Cloud Platform Integration)
1 -
SAP Data Quality Management
2 -
SAP ECC
1 -
SAP ERP
2 -
SAP Maintenance resource scheduling
2 -
SAP MDG Data Quality Management
1 -
SAP MDG DQM
1 -
SAP MDM
1 -
SAP Mentors
1 -
SAP MM
1 -
SAP Note 390635
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP S4HANA Public Cloud Finance
1 -
sap security
1 -
SAP Subcontracting Process
1 -
SAP Upgrade Automation
1 -
SAP WCM
1 -
SAP Work Clearance Management
1 -
Schedule Agreement
1 -
SD (Sales and Distribution)
1 -
SDM
1 -
security
2 -
Settlement Management
1 -
soar
2 -
Sourcing and Procurement
1 -
SSIS
1 -
SU01
1 -
SUM2.0SP17
1 -
SUMDMO
1 -
Teams
2 -
Time Management
1 -
Transpo
1 -
User Administration
1 -
User Participation
1 -
Utilities
1 -
va01
1 -
vendor
1 -
vl01n
1 -
vl02n
1 -
WCM
1 -
X12 850
1 -
xlsx_file_abap
1 -
YTD|MTD|QTD in CDs views using Date Function
1
- « Previous
- Next »
- Blog Series: SAP S/4 HANA Cloud Public Edition – 02 TM Freight Accounting and Material Valuation in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by Members
- SAP S/4HANA Cloud Public Edition - Finance-Cost Accounting - Frequently Asked Questions in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- SAP S/4HANA Cloud Public Edition - Finance-General Ledger Accounting - Frequently Asked Questions in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Connection string Crystal reports in SAP B1 HANA version 10 - Calculation views in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
- Custom Analytical Queries as an alternative for LIS in SAP S/4HANA Production Planning (PP) in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 10 | |
| 6 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 1 |