- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Enterprise Resource Planning
- ERP Blogs by Members
- Application Link Enabling (ALE)
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Introduction
Application Link Enabling (ALE)
ALE stands for Application Link Enabling. ALE in SAP is used for exchanging business data between different systems. This form of communication requires IDOC interface. The IDoc interface is made up of the definition of a data structure and the processing logic of this data structure. The data structure is the Idoc.
If packet is being created in Q system and sent to P system then, outbound parameters of PCLNT100 will be checked in Q system and inbound parameters of QCLNT100 will be checked in P system.
Prerequisites
The ID & Password should be in working condition and we should be able to access both the clients in the system.
Set-up
1 Settings on Sender side (Q):
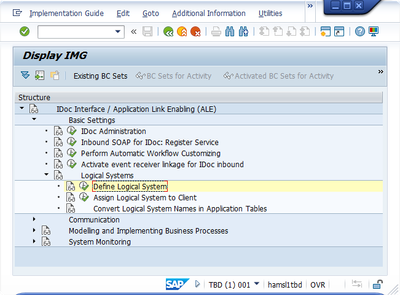
1.1 Defining Logical System
T-code: SALE
IDoc Interface / Application Link Enabling (ALE) -> Basic Settings -> Logical Systems -> Define Logical System
QCLNT100: Logical system for sender system (Q Client 100) - Sender
PCLNT100: Logical system for receiver system (P Client 100) - Receiver
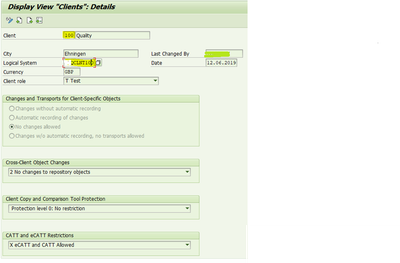
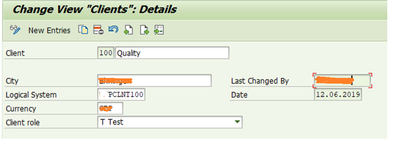
1.2Assigning Logical system to Client
T-code: SCC4
- Select one line.
- Choose: Goto -> Details.
- The 'Client Details' screen appears. In the field Logical system, enter the name of the logical system to which you want to assign the selected client.
- Save your entries.
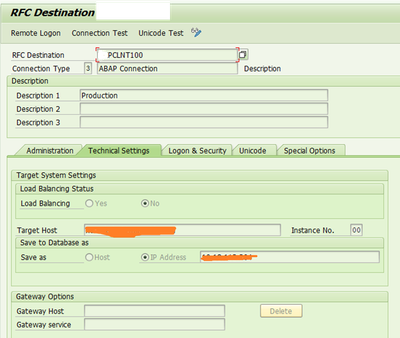
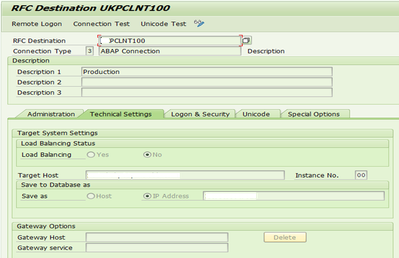
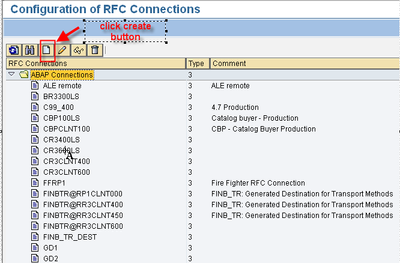
1.3 RFC destination for Partner
T-code: SM59
- Select one of the types (for example, SAP connections) and choose Edit -> create
- Enter the parameters required for that type.
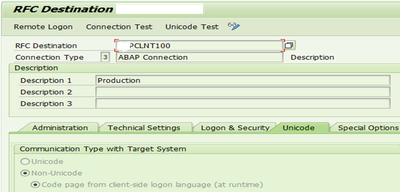
- For an SAP connection, these are, for example, the name of the RFC destination, the name of the partner system, logon parameters (see example).
|
Specify message server in target host.
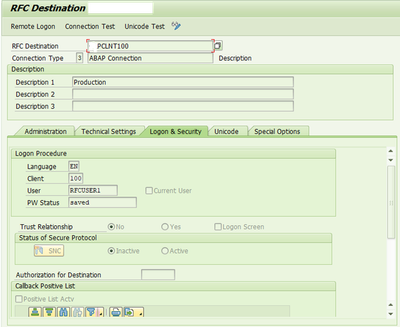
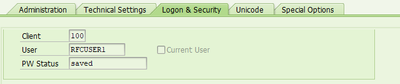
On Log On and security Tab, Enter User and password details of user from receiver. For the current set up, user is PDR_BATCH and a password is set as provided by administrator.
Select Unicode connection type for transferring the data as it is.
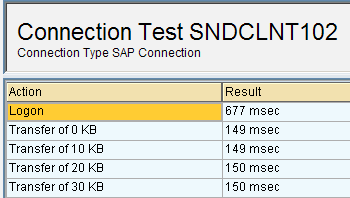
Test the connection just created by clicking on ‘Connection Test’.
|
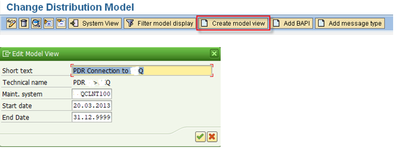
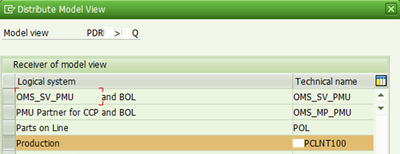
1.4 Maintain Distribution model.
T-code: BD64
The distribution model consists of separate model views in which all the associated, cross-system message flows in your organization can be defined. These views must be distributed to the receiving systems.
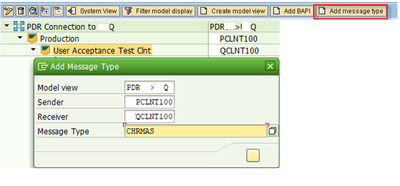
In addition to the message types for the object, you need two other message types that have been introduced for PLM product data distribution.
- Message type UPSMAS (distribution packet)
Distributes the ALE distribution packet to the recipient systems from the central system.
- Message type UPSRCP (receipts)
Sends receipts via ALE distribution packets from the recipient systems for product data distribution to the central sending system.
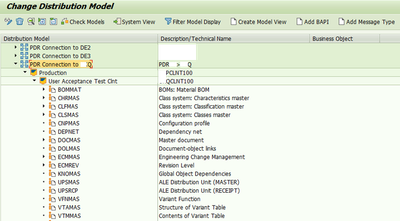
Distribution model after adding all relevant message types is shown below.
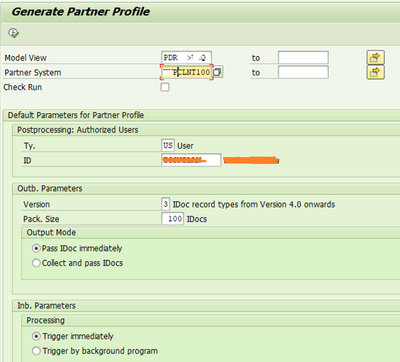
1.5 Generate Partner Profile
Partner profile can be generated either by WE20 manually or automatically by WE82. From distribution model screen also the partner profile can be generated. To generate from distribution model screen, select generate partner profile.
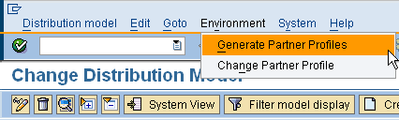
|
Check in WE20 for partner profile created above and correct the process codes generated for the inbound messages for receiving partner.
2 Settings on Receiver Side (P Client 100)
2.1 Define logical systems:
T-code: SCC4
Define logical systems for both sender and receiver as in previous section for sending side. Assign logical system for receiver (P Client 100) to client.
2.2 Maintain RFC Destination
T-code: SM59
Use the steps similar to those in section 2.1.3.
Maintain the User and password details for P system as provided by the Basis team. In this set up, the user is RFCUSER1.
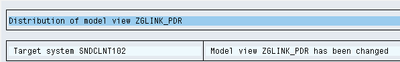
2.3 Distributing and Transporting Model Views
Model views are distributed between systems on the same level (development systems, test systems, productive systems) via the Change and Transport System. You have to create a transport request for the model view from sending system. Choose Edit -> Model view -> Distribute.
Go to transaction BD64 in RR3.
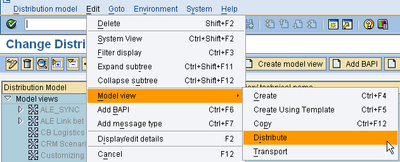
|
Now go to BD64 in P (Production System), the model is distributed from Q to P. Correct the entries/process codes if necessary and Generate Partner profile for sending system. You can view partner profile in WE20.
Conclusion
ALE in SAP improves and optimizes the business performance ensuring good flow of data between systems through RFC and so on. It is an versatile technology which is required to meet some specific needs in SAP to SAP systems or external connectivity.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- MAN Production Planning (PP),
- NW ABAP Integration Technology (ALE)
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
"mm02"
1 -
A_PurchaseOrderItem additional fields
1 -
ABAP
1 -
ABAP Extensibility
1 -
ACCOSTRATE
1 -
ACDOCP
1 -
Adding your country in SPRO - Project Administration
1 -
Advance Return Management
1 -
AI and RPA in SAP Upgrades
1 -
Approval Workflows
1 -
Ariba
1 -
ARM
1 -
ASN
1 -
Asset Management
1 -
Associations in CDS Views
1 -
auditlog
1 -
Authorization
1 -
Availability date
1 -
Azure Center for SAP Solutions
1 -
AzureSentinel
2 -
Bank
1 -
BAPI_SALESORDER_CREATEFROMDAT2
1 -
BRF+
1 -
BRFPLUS
1 -
Bundled Cloud Services
1 -
business participation
1 -
Business Processes
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Carbon
1 -
Cental Finance
1 -
CFIN
1 -
CFIN Document Splitting
1 -
Cloud ALM
1 -
Cloud Integration
1 -
condition contract management
1 -
Connection - The default connection string cannot be used.
1 -
Custom Table Creation
1 -
Customer Screen in Production Order
1 -
Customizing
1 -
Data Quality Management
1 -
Date required
1 -
Decisions
1 -
desafios4hana
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Direct Outbound Delivery
1 -
DMOVE2S4
1 -
EAM
1 -
EDI
3 -
EDI 850
1 -
EDI 856
1 -
edocument
1 -
EHS Product Structure
1 -
Emergency Access Management
1 -
Energy
1 -
EPC
1 -
Financial Operations
1 -
Find
1 -
FINSSKF
1 -
Fiori
1 -
Flexible Workflow
1 -
Gas
1 -
Gen AI enabled SAP Upgrades
1 -
General
1 -
generate_xlsx_file
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
HomogeneousDMO
1 -
How to add new Fields in the Selection Screen Parameter in FBL1H Tcode
1 -
IDOC
2 -
Integration
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
Ledger Combinations in SAP
1 -
LogicApps
2 -
low touchproject
1 -
Maintenance
1 -
management
1 -
Material creation
1 -
Material Management
1 -
MD04
1 -
MD61
1 -
methodology
1 -
Microsoft
2 -
MicrosoftSentinel
2 -
Migration
1 -
mm purchasing
1 -
MRP
1 -
MS Teams
2 -
MT940
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
Notifications
1 -
Oil
1 -
open connectors
1 -
Order Change Log
1 -
ORDERS
2 -
OSS Note 390635
1 -
outbound delivery
1 -
outsourcing
1 -
PCE
1 -
Permit to Work
1 -
PIR Consumption Mode
1 -
PIR's
1 -
PIRs
1 -
PIRs Consumption
1 -
PIRs Reduction
1 -
Plan Independent Requirement
1 -
POSTMAN
1 -
Premium Plus
1 -
pricing
1 -
Primavera P6
1 -
Process Excellence
1 -
Process Management
1 -
Process Order Change Log
1 -
Process purchase requisitions
1 -
Product Information
1 -
Production Order Change Log
1 -
purchase order
1 -
Purchase requisition
1 -
Purchasing Lead Time
1 -
Redwood for SAP Job execution Setup
1 -
RISE with SAP
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
Rizing
1 -
S4 Cost Center Planning
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4HANA
3 -
S4HANACloud audit
1 -
Sales and Distribution
1 -
Sales Commission
1 -
sales order
1 -
SAP
2 -
SAP Best Practices
1 -
SAP Build
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP CI
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP CPI
1 -
SAP Data Quality Management
1 -
SAP ERP
1 -
SAP Maintenance resource scheduling
2 -
SAP Note 390635
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Upgrade Automation
1 -
SAP WCM
1 -
SAP Work Clearance Management
1 -
Schedule Agreement
1 -
SDM
1 -
security
2 -
Settlement Management
1 -
soar
2 -
Sourcing and Procurement
1 -
SSIS
1 -
SU01
1 -
SUM2.0SP17
1 -
SUMDMO
1 -
Teams
2 -
Time Management
1 -
User Administration
1 -
User Participation
1 -
Utilities
1 -
va01
1 -
vendor
1 -
vl01n
1 -
vl02n
1 -
WCM
1 -
X12 850
1 -
xlsx_file_abap
1 -
YTD|MTD|QTD in CDs views using Date Function
1
- « Previous
- Next »
- Preferred Success Round Table Discussion with SAP Customers on 29th April @ SAP NOW India. in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- S4H OnPrem 2022 Initial SP - Assign Handling Unit to Outbound Delivery by BAPI in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
- Ways to create a purchase order in SAP in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by Members
- Recap of SAP S/4HANA 2023 Highlights Webinar: Finance in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- SAP Activate methodology Prepare and Explore phases in the context of SAFe. in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 |