- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Financial Management
- Financial Management Blogs by Members
- Security by Default vs Security by Design
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
It's a debate worth delving into at any time! Should organizations adhere to the default security configurations within an application, or should they design their own to enhance security?
In today's digital world, keeping sensitive business information safe is more critical than ever. As organizations rely heavily on SAP systems which are connected with many other applications to manage their operations, the need for strong security measures is paramount. One key debate in this realm is whether organizations should adhere to standard security configurations that the applications provide or design additional layers to enhance security?
Let's break down these two approaches: "Security by Default" and "Security by Design."
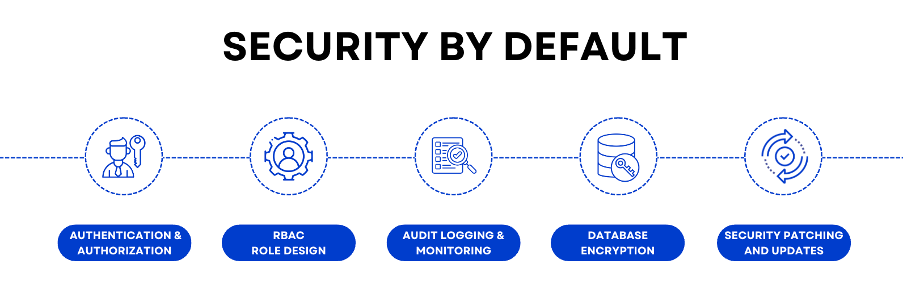
As the name says, "Security by Default" essentially means sticking to the pre-established security settings provided by SAP or other applications. I am limiting this blog to SAP application as the subject itself is vast. SAP application has the following Security measures by default:
- User Authentication and Authorization – User log’s in to the application and executes the transaction codes or Apps that are assigned to his/her profile.
- RBAC Role design – With Role based Access, you can provide the authorizations that are necessary to the user to perform his/her job duties. Creating various types of roles in SAP is easy and many solutions are available such as SAP GRC Access Control to streamline this process.
- Audit Logging and Monitoring – SAP logs most of the activities that are happening in the SAP system in the form of logs. These can be accessed at a later point and also connected to various solutions such as SAP ETD, or a SIEM based solution
- Encryption – If you are on SAP HANA, you can utilize HANA DB encryption capabilities. Read through this blog.
- Security Patching and Updates – SAP also releases patches and updates periodically to secure the SAP system. It is highly recommended to patch the system. Refer to SAP patch day website to understand more about the critical security patches, their release information and so on.
While default security capabilities provide a certain level of assurance that applications are protected, the question arises: is this level of security truly sufficient? If you're prepared to answer "yes," it's worth revisiting your stance in light of the latest 2024 Cyber Crime Statistics (updated February 2024).
- The most common cyber threat facing businesses and individuals is phishing.
- Nearly 1 billion emails were exposed in a single year, affecting 1 in 5 internet users.
- Around 236.1 million ransomware attacks occurred globally in the first half of 2022.
- 39% of UK businesses reported suffering a cyberattack in 2022.
- 32% of UK businesses reported suffering a cyber-attack or breach in 2023. For medium businesses, this rises to 59%. 69% of large businesses reported an attack.
- The average cost of a breach against medium and large UK businesses is £4960 as of December 2023.
- The most common form of cybercrime in India is financial fraud. This accounted for 75% of cybercrime in India between 2020 and 2023, with a high point of over 77% of crimes committed during the period.
- The average cost of a cyber breach in 2022 was $4.35 million.
- Supply chain attacks are seen by 60% of C-Suite executives as the most likely type of cyber threat that would affect their business.
- Online payment fraud is predicted to cost businesses $343 billion between 2023-2027.
Now let’s understand Security by Design and how it can help in securing the system with additional layers of security.
Embracing Security by Design
"Security by Design" goes beyond implementing the standard security measures. It integrates security considerations into the entire development lifecycle of SAP solutions. It emphasizes proactively identifying and addressing security risks at every stage, from design and development to deployment and maintenance.
How to implement Security by Design?
- Code Reviews and Security Testing: Performing comprehensive code reviews and security testing throughout the development lifecycle helps identify and remediate security vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SAP applications. This includes conducting static code analysis, dynamic application security testing (DAST), and penetration testing to assess the resilience of SAP systems against various cyber threats.
- Secure Development Practices: Adhering to secure coding practices and guidelines is essential for developing robust and resilient SAP applications. Developers should be trained in secure coding techniques and follow secure coding standards recommended by SAP and various industry frameworks to minimize the risk of introducing vulnerabilities into the software.
- Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response: Implementing robust monitoring capabilities and incident response procedures allows organizations to detect and respond to security incidents promptly. Continuous monitoring helps identify anomalous activities and potential security breaches, enabling timely intervention and mitigation measures to minimize the impact on SAP systems and data. Many SAP solutions and GRC solutions can be utilized to monitor the systems and perform incident response.
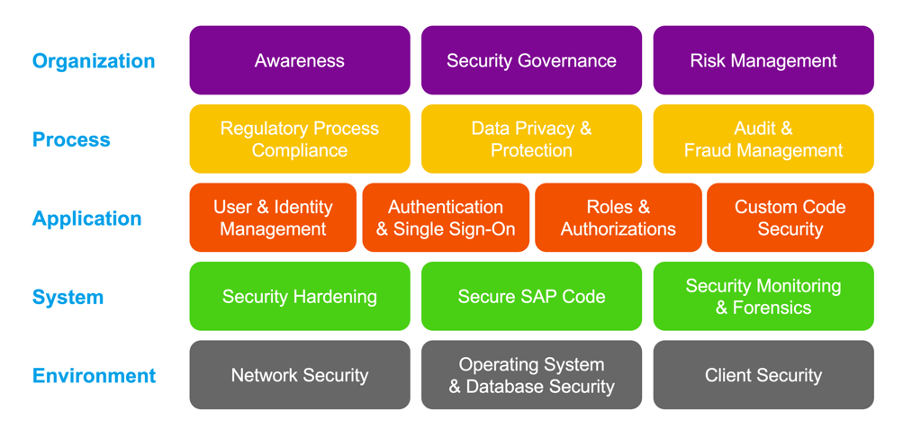
Identifying and implementing various solutions to secure the system is a tedious task. It is advisable to adapt to a framework/model. One such model is the Security Operations Map (SOM), which serves as a reference model structuring the broad areas of cybersecurity. It establishes a solid foundation for conducting a comprehensive 360-degree review of cybersecurity and compliance practices within customer landscapes.
The SOM was crafted based on SAP's insights into security needs and branches. However, it can also be aligned with other well-known cybersecurity frameworks like the National Institute of Standards and Technology's Cybersecurity Framework or the German Federal Cyber Security Authority's IT-Grundschutz. What sets SOM apart is its global applicability within the SAP environment. Read the SAP Insider article that details more about SOM.
Security Operations Map (SOM) as per NIST framework (Source: SAP)
Wait!! Am I endorsing the concept of Security by Design?
Not at all. Infact, the answer isn't straightforward and largely depends on various factors, including the organization's risk tolerance, regulatory requirements, and the nature of its operations. While sticking to default configurations can offer simplicity and consistency, it may not provide the level of protection needed in high-risk environments or industries with stringent compliance mandates.
On the other hand, designing custom security measures allows organizations to address specific threats and vulnerabilities effectively. However, this approach requires careful planning, expertise, and ongoing maintenance to ensure that security controls remain robust and adaptive to evolving threats.
In conclusion, there's no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to securing SAP environments. Organizations must carefully weigh the pros and cons of both approaches and develop a security strategy that strikes the right balance between effectiveness, efficiency, and compliance. Whether opting for Security by Default or Security by Design, the ultimate goal remains the same: safeguarding critical data and infrastructure from cyber threats in an ever-changing digital landscape.
Additional References:
I suggest you to go through my previous blog - Beyond Firewalls: A Holistic Strategy for Application and Data Security. The Security Pentagon!
- SAP Managed Tags:
- Defense and Security,
- Governance, Risk, Compliance (GRC), and Cybersecurity,
- Security
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
2023 Upgrade
1 -
Accounting & Financial Close
1 -
Accounting and Financial Close
1 -
Assign Missing Authorization Objects
1 -
Bank Reconciliation Accounts
1 -
CLM
1 -
EAM
1 -
Emergency Access Management
1 -
FFID
1 -
FI-AA
1 -
FIN Asset Management
1 -
FIN-CS
1 -
FINANCE
2 -
GRIR
1 -
Group Reporting
1 -
Invoice Printing Lock
2 -
Mapping of Catalog & Group
1 -
Mapping with User Profile
1 -
matching concept and accounting treatment
1 -
Oil & Gas
1 -
Parameter 4026
1 -
Payment Batch Configurations
1 -
Public Cloud
1 -
Revenue Recognition
1 -
review booklet
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4 HANA 2022
1 -
S4 HANA On-Premise
1 -
S4HANA
1 -
SAP BRIM
1 -
SAP CI
1 -
SAP FICO
1 -
SAP RAR
1 -
SAP S4HANA
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud for Finance
1 -
SAP Treasury Hedge Accounting
1 -
Z Catalog
1 -
Z Group
1
- Parameter 4026: Transforming Your Approach to EAM Application in SAP GRC Access Control in Financial Management Blogs by Members
- TRS_SEC_ACC default field for ftr_create (field VWSFHA-RLDEPO) in Financial Management Q&A
- GRC Tuesdays: Takeaways from the 2024 Internal Controls, Compliance and Risk Management Conference in Financial Management Blogs by SAP
- Digital Banking Add-on Package for RISE and GROW with SAP in Financial Management Blogs by SAP
- GRC Process Control: How CCM can be leveraged to monitor HANA Databases in Financial Management Q&A